
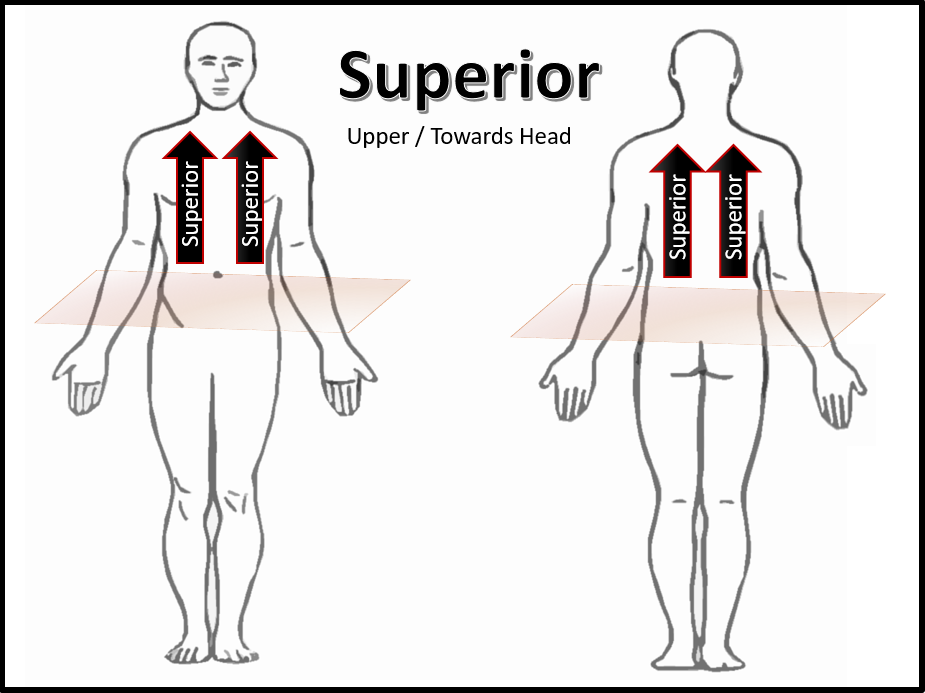
The appendicular part consists of the limbs (appendages) attached to the body’s axis. The axial part makes up the main axis of the body and includes the head, neck, and trunk. The two main divisions of the body are its axial and appendicular parts. Deep (internal)– Away from the body surfaceĭirectional terms allow us to explain where one body part is when compared to another.Superficial (external)– toward or at the body surface.Distal– away from the origin of a body part or point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk.Proximal– closer to the origin of the body part or point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk.Intermediate– between a medial and lateral position.Lateral– away from the midline of the body.Medial– toward or at the midline of the body.Dorsal (posterior)– toward or at the back of the body behind.Ventral (anterior)– toward or at the front of the body in front of.Inferior (caudal)– away from the head or toward the lower part of the body below.Superior (cranial)– toward the head or upper part of the body above.It’s important to understand the anatomical position because most directional terms are based off it. In the anatomical position, the body is erect, the palms of the hand face forward, the thumbs point away from the body, and the feet are slightly apart. The anatomical reference point is a standard body position called the anatomical position. In order to describe body parts and positions correctly, the medical community has developed a set of anatomical positions and directional terms widely used in the healthcare industry. We’ll begin by going over “anatomical position and directional terms”. In order to provide exquisite care and understand the inner workings of the human body, anatomical terminology is a necessity. The healthcare industry has its own terminology, especially anatomy and physiology. Vertical axis - passes vertically from inferior to superior and is formed by the intersection of the sagittal and frontal planes.Anatomical position and directional terms.The feet are spaced slightly apart with the toes pointing forward. The palms are facing forward with the fingers extended, and the thumbs are pointing away from the body. Frontal axis - passes horizontally from left to right and is formed by the intersection of the frontal and transverse planes. The anatomical position is a standing position, with the head facing forward and the arms to the side.Sagittal axis - passes horizontally from posterior to anterior and is formed by the intersection of the sagittal and transverse planes.Movement at the joint takes place in a plane about an axis. For example, if a person jumped directly up and then down, their body would be moving through the transverse plane in the coronal and sagittal planes.Īn axis is a straight line around which an object rotates. So by moving through the transverse plane, movement travels from head to toe. When describing anatomical motion, these planes describe the axis along which an action is performed. Unlike the situation in other vertebrates, the limbs are placed in positions reminiscent of the supine position imposed on cadavers during autopsy. In standard anatomical position, the human body is standing erect and at rest. It is parallel to the ground, which (in humans) separates the superior from the inferior, or put another way, the head from the feet. The standard anatomical position in a male and female. A transverse plane, also known as an axial plane or cross-section, divides the body into cranial (head) and caudal (tail) portions.A coronal or frontal plane is perpendicular to the ground and divides the body into dorsal (posterior or back) and ventral (anterior or front) portions.Median can also refer to the midsagittal plane of other structures, such as a digit. navel or spine), and all other sagittal planes (also referred to as parasagittal planes) are parallel to it. it would pass through the midline structures (e.g. The midsagittal or median plane is in the midline i.e.
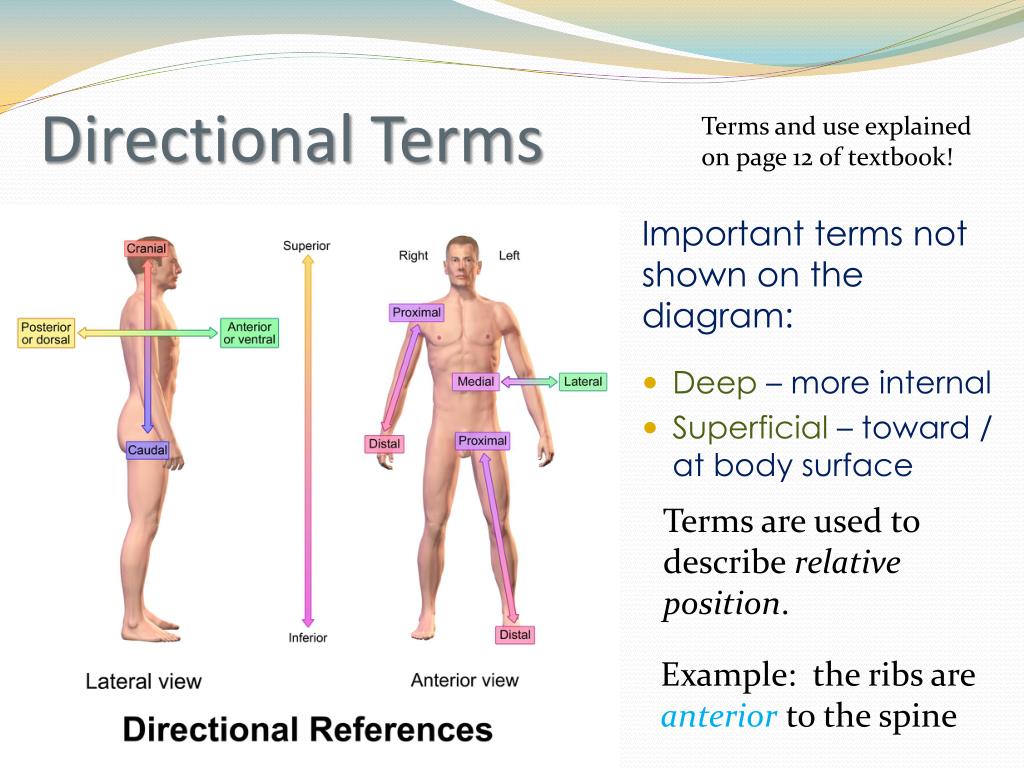

Three basic reference planes are used in anatomy:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
